Estimate geodetic time series from the Nevada Geodetic Laboratory
Source:vignettes/estimate_geodetic_time_series_from_ngl.Rmd
estimate_geodetic_time_series_from_ngl.RmdModel and estimator
This vignette builds on the general framework described in the vignettes “Estimate linear models with dependent errors” and “Estimate linear models with dependent errors and missing observations”. We do not repeat the full model, missingness mechanism, or estimation details here. Please refer to these vignettes for the formal setup, and use this one as a hands-on guide for geodetic time series from the Nevada Geodetic Laboratory.
Estimating tectonic velocities and crustal uplift
While the GMWMX, as described above and in more detail in Voirol et al. (2024), is a general method for
estimating large linear models with complex dependence structures in
presence of missing observations, the gmwmx2 R
package allows to estimate tectonic velocities and crustal uplift from
position time series in graticule distance (GD) coordinates provided by
the Nevada Geodetic Laboratory (Blewitt 2024;
Blewitt, Hammond, and Kreemer 2018).
Trajectory model
To estimate the trajectory model (see, e.g., Bevis and Brown (2014) for more details), we construct the design matrix such that the -th component of the vector can be described as follows, with representing the ordered time point (epoch) in Modified Julian Date and representing the reference epoch located exactly in the middle of the start and end points of the time series:
where is the initial position at the reference epoch , is the velocity parameter, and and are the periodic motion parameters ( and represent the annual and semi-annual seasonal terms, respectively with and ). The offset terms model earthquakes, equipment changes, or human intervention, in which is the magnitude of the step at epochs , is the total number of offsets, and is the Heaviside step function defined as . The last term allows us to model post-seismic deformation (see, e.g., Sobrero et al. (2020)) where is the number of post-seismic relaxation times specified, is the time when the relaxation starts in Modified Julian Date (MJD), is the relaxation period in days for the post-seismic relaxation , and is the amplitude of the transient. Note that by default the estimates of the functional parameters are provided in units/day.
When loading data from a specific station using
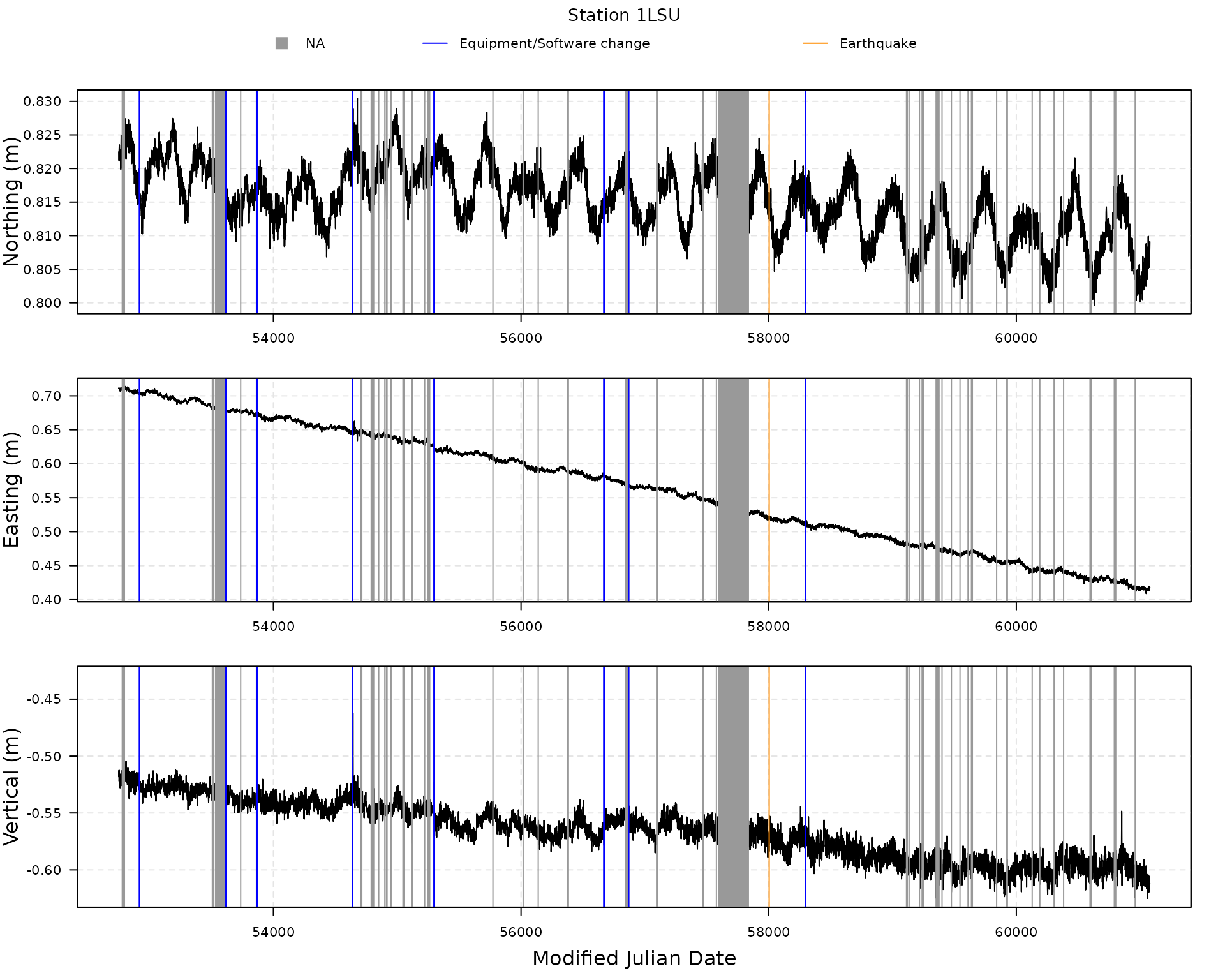
gmwmx2::download_station_ngl(), we extract from the Nevada
Geodetic Laboratory the position time series in GD coordinates, the time
steps associated with equipment or software changes, and the time steps
associated with earthquakes near the station. All these objects are
stored in an object of class gnss_ts_ngl.
When applying the function gmwmx2::gmwmx2() to an object
of class gnss_ts_ngl, we construct the design matrix
by considering an offset term for all equipment or software change steps
and all earthquakes indicated by the NGL. We also specify a post-seismic
relaxation term for all earthquakes indicated by the NGL. If no
relaxation time is specified in the argument
vec_earthquakes_relaxation_time, we use a default
relaxation time of
days.
Stochastic model
It is generally recognized that noise in GNSS time series is best described by a combination of colored noise plus white noise (He et al. 2017; Langbein 2008; Williams et al. 2004; Bos et al. 2013), where the white noise generally models noise at high frequencies and the colored noise models the lower frequencies of the spectrum.
In gmwmx2, you can pass any valid stochastic model to
the estimator: either a single time-series model (e.g.,
wn(), ar1(), pl(),
matern(), rw(), flicker()) or a
composite sum model built with + (e.g.,
wn() + pl() or wn() + ar1() + rw()). This
makes the stochastic specification very general and easy to adapt to
your application.
Example of estimation
Let us showcase how to estimate tectonic velocity for one specific component (North, East, or Vertical) of one station.
First, load the gmwmx2 package.
Download a station from Nevada Geodetic Laboratory
station_data <- download_station_ngl("1LSU")Estimate models on station data
## GMWMX fit GNSS Times Series (Nevada Geodetic Laboratory)
## Estimate Std.Error CI.Lower CI.Upper
## Intercept 8.156e-01 1.788e-04 8.152e-01 8.159e-01
## Trend -1.090e-06 3.588e-08 -1.160e-06 -1.019e-06
## Sin (Annual) -5.216e-04 2.092e-05 -5.626e-04 -4.806e-04
## Cos (Annual) -4.129e-03 2.091e-05 -4.170e-03 -4.088e-03
## Sin (Semi-Annual) 1.089e-03 2.057e-05 1.049e-03 1.129e-03
## Cos (Semi-Annual) -4.455e-04 2.057e-05 -4.858e-04 -4.051e-04
## Jump: MJD 52920 4.958e-04 1.157e-04 2.691e-04 7.226e-04
## Jump: MJD 53619 -3.057e-03 9.985e-05 -3.253e-03 -2.861e-03
## Jump: MJD 53866 -5.586e-04 9.908e-05 -7.528e-04 -3.644e-04
## Jump: MJD 54637 -2.499e-04 7.663e-04 -1.752e-03 1.252e-03
## Jump: MJD 54640 6.393e-03 7.666e-04 4.890e-03 7.895e-03
## Jump: MJD 55300 -2.496e-03 7.267e-05 -2.639e-03 -2.354e-03
## Jump: MJD 56671 -1.193e-03 1.057e-04 -1.400e-03 -9.857e-04
## Jump: MJD 56868 1.120e-03 1.055e-04 9.134e-04 1.327e-03
## Jump: MJD 58298 3.321e-03 1.753e-04 2.977e-03 3.664e-03
## Jump: MJD 58004 1.137e-03 1.162e-04 9.096e-04 1.365e-03
## Earthquake: MJD 58004 -7.135e-03 2.909e-04 -7.705e-03 -6.565e-03
##
## Missingness model
## Proportion missing : 0.0584
## p1 : 0.0073
## p2 : 0.1173
## p* : 0.9416
##
## Stochastic model
## Model : White Noise
## Parameters : sigma2 = 1.65e-06
##
## Runtime (seconds)
## Total : 2.5790
plot(fit1)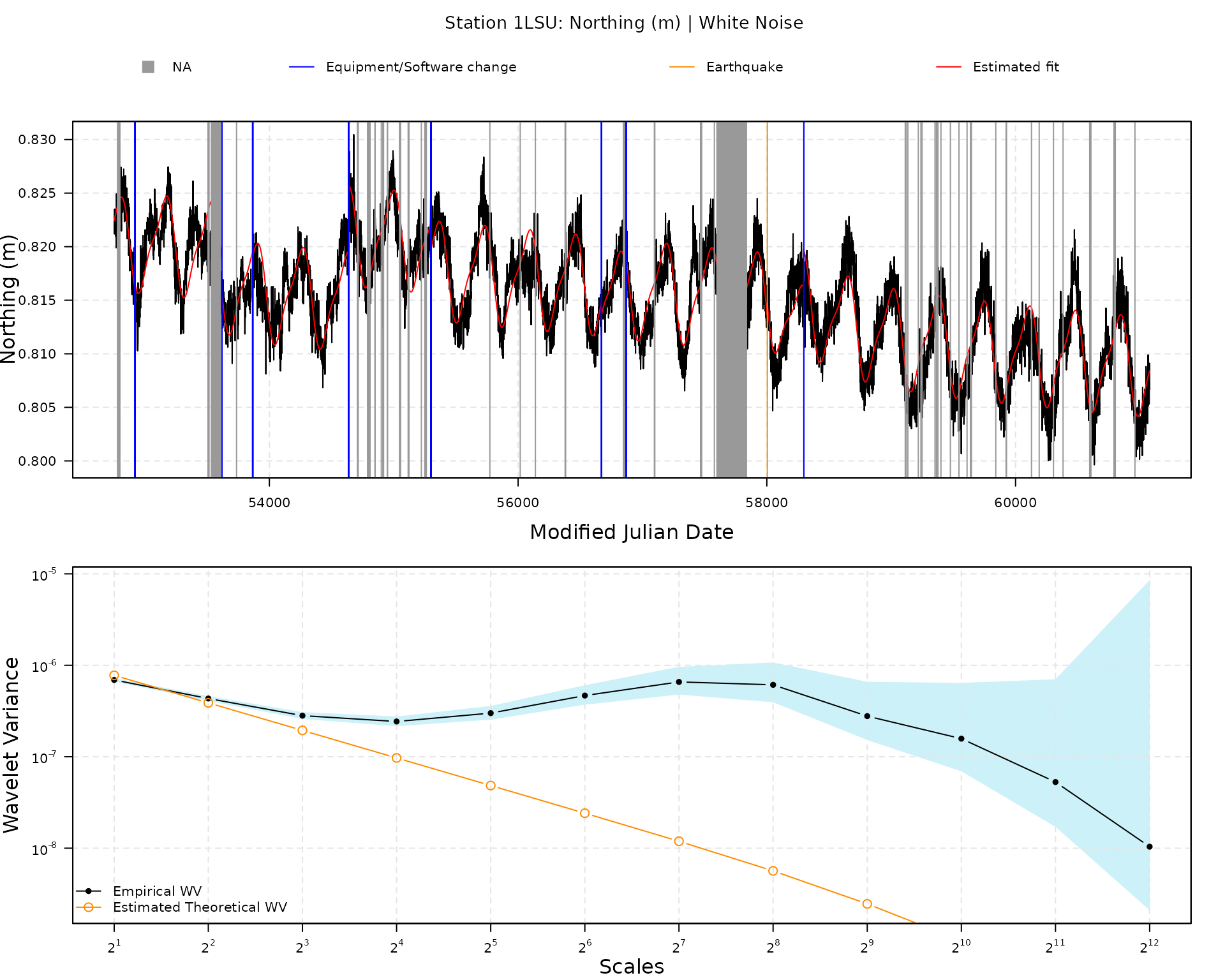
## GMWMX fit GNSS Times Series (Nevada Geodetic Laboratory)
## Estimate Std.Error CI.Lower CI.Upper
## Intercept 8.156e-01 5.429e-01 -2.485e-01 1.880e+00
## Trend -1.090e-06 1.396e-05 -2.846e-05 2.628e-05
## Sin (Annual) -5.216e-04 8.143e-03 -1.648e-02 1.544e-02
## Cos (Annual) -4.129e-03 8.144e-03 -2.009e-02 1.183e-02
## Sin (Semi-Annual) 1.089e-03 7.825e-03 -1.425e-02 1.643e-02
## Cos (Semi-Annual) -4.455e-04 7.824e-03 -1.578e-02 1.489e-02
## Jump: MJD 52920 4.958e-04 4.439e-02 -8.650e-02 8.749e-02
## Jump: MJD 53619 -3.057e-03 3.861e-02 -7.873e-02 7.262e-02
## Jump: MJD 53866 -5.586e-04 3.832e-02 -7.567e-02 7.455e-02
## Jump: MJD 54637 -2.499e-04 1.267e-01 -2.485e-01 2.480e-01
## Jump: MJD 54640 6.393e-03 1.267e-01 -2.420e-01 2.548e-01
## Jump: MJD 55300 -2.496e-03 2.835e-02 -5.805e-02 5.306e-02
## Jump: MJD 56671 -1.193e-03 4.077e-02 -8.110e-02 7.872e-02
## Jump: MJD 56868 1.120e-03 4.067e-02 -7.859e-02 8.083e-02
## Jump: MJD 58298 3.321e-03 6.656e-02 -1.271e-01 1.338e-01
## Jump: MJD 58004 1.137e-03 4.488e-02 -8.683e-02 8.911e-02
## Earthquake: MJD 58004 -7.135e-03 1.108e-01 -2.243e-01 2.101e-01
##
## Missingness model
## Proportion missing : 0.0584
## p1 : 0.0073
## p2 : 0.1173
## p* : 0.9416
##
## Stochastic model
## Sum of 2 processes
## [1] White Noise
## Estimated parameters : sigma2 = 8.165e-07
## [2] Stationary PowerLaw
## Estimated parameters : kappa = -1, sigma2 = 9.708e-07
##
## Runtime (seconds)
## Total : 2.8893
plot(fit2)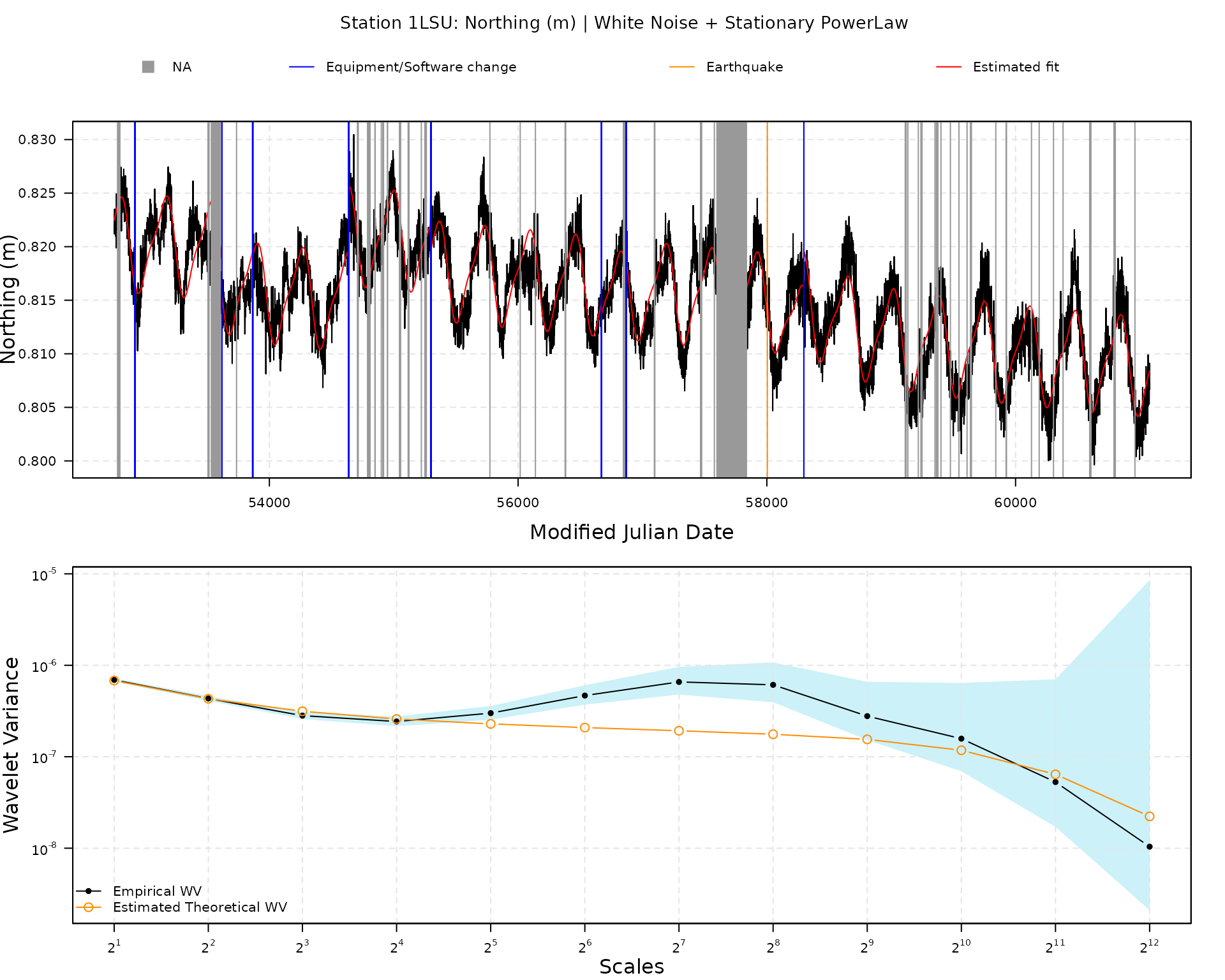
## GMWMX fit GNSS Times Series (Nevada Geodetic Laboratory)
## Estimate Std.Error CI.Lower CI.Upper
## Intercept 8.156e-01 2.298e-03 8.111e-01 8.201e-01
## Trend -1.090e-06 5.367e-07 -2.142e-06 -3.774e-08
## Sin (Annual) -5.216e-04 1.246e-04 -7.659e-04 -2.773e-04
## Cos (Annual) -4.129e-03 1.279e-04 -4.380e-03 -3.878e-03
## Sin (Semi-Annual) 1.089e-03 8.826e-05 9.160e-04 1.262e-03
## Cos (Semi-Annual) -4.455e-04 8.823e-05 -6.184e-04 -2.725e-04
## Jump: MJD 52920 4.958e-04 9.597e-04 -1.385e-03 2.377e-03
## Jump: MJD 53619 -3.057e-03 1.001e-03 -5.019e-03 -1.095e-03
## Jump: MJD 53866 -5.586e-04 1.020e-03 -2.559e-03 1.441e-03
## Jump: MJD 54637 -2.499e-04 1.594e-03 -3.374e-03 2.875e-03
## Jump: MJD 54640 6.393e-03 1.581e-03 3.294e-03 9.492e-03
## Jump: MJD 55300 -2.496e-03 1.066e-03 -4.586e-03 -4.063e-04
## Jump: MJD 56671 -1.193e-03 1.114e-03 -3.377e-03 9.908e-04
## Jump: MJD 56868 1.120e-03 1.101e-03 -1.038e-03 3.279e-03
## Jump: MJD 58298 3.321e-03 1.458e-03 4.623e-04 6.179e-03
## Jump: MJD 58004 1.137e-03 1.493e-03 -1.790e-03 4.064e-03
## Earthquake: MJD 58004 -7.135e-03 3.175e-03 -1.336e-02 -9.126e-04
##
## Missingness model
## Proportion missing : 0.0584
## p1 : 0.0073
## p2 : 0.1173
## p* : 0.9416
##
## Stochastic model
## Sum of 2 processes
## [1] White Noise
## Estimated parameters : sigma2 = 8.156e-07
## [2] Flicker
## Estimated parameters : sigma2 = 9.725e-07
##
## Runtime (seconds)
## Total : 6.0101
plot(fit3)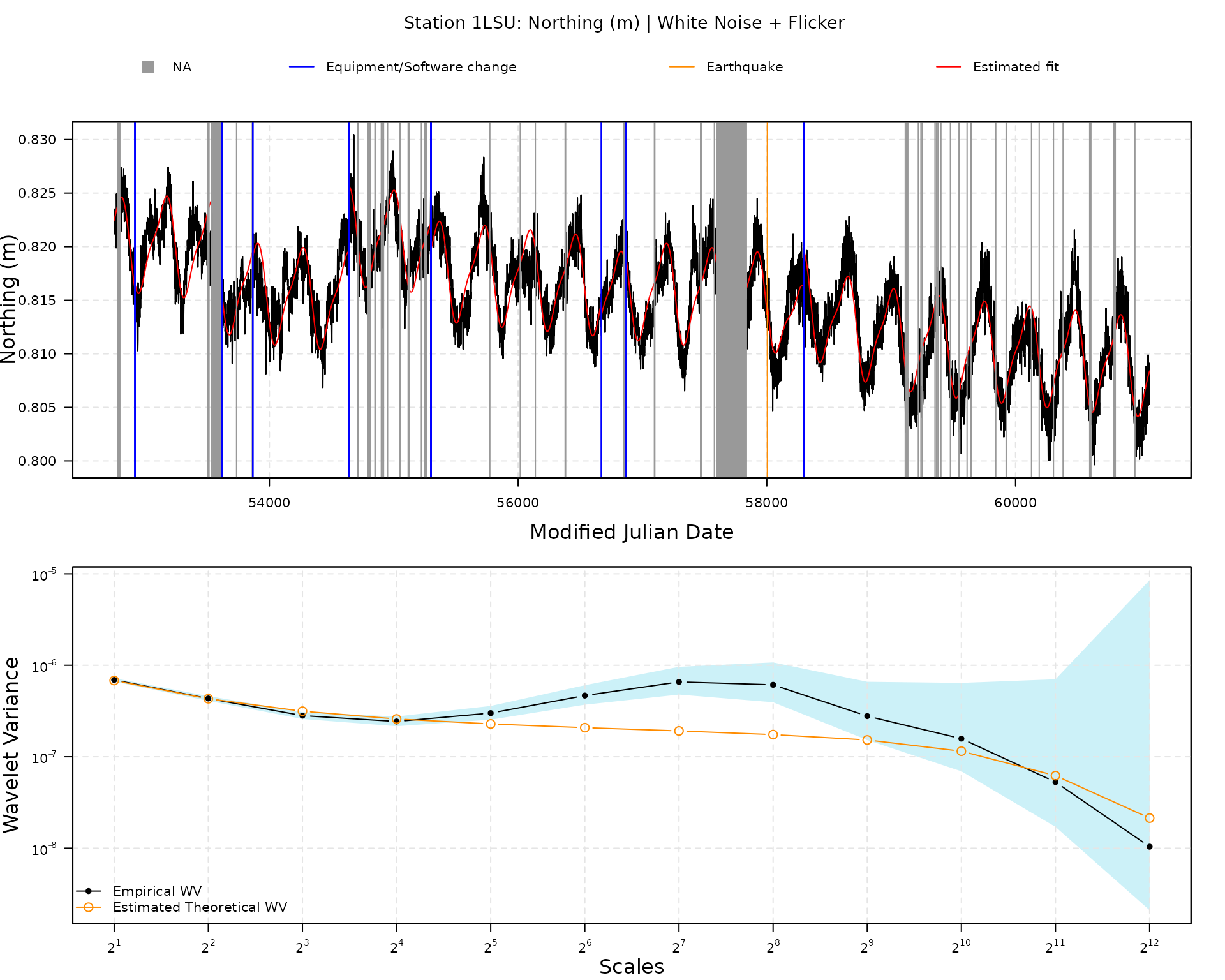
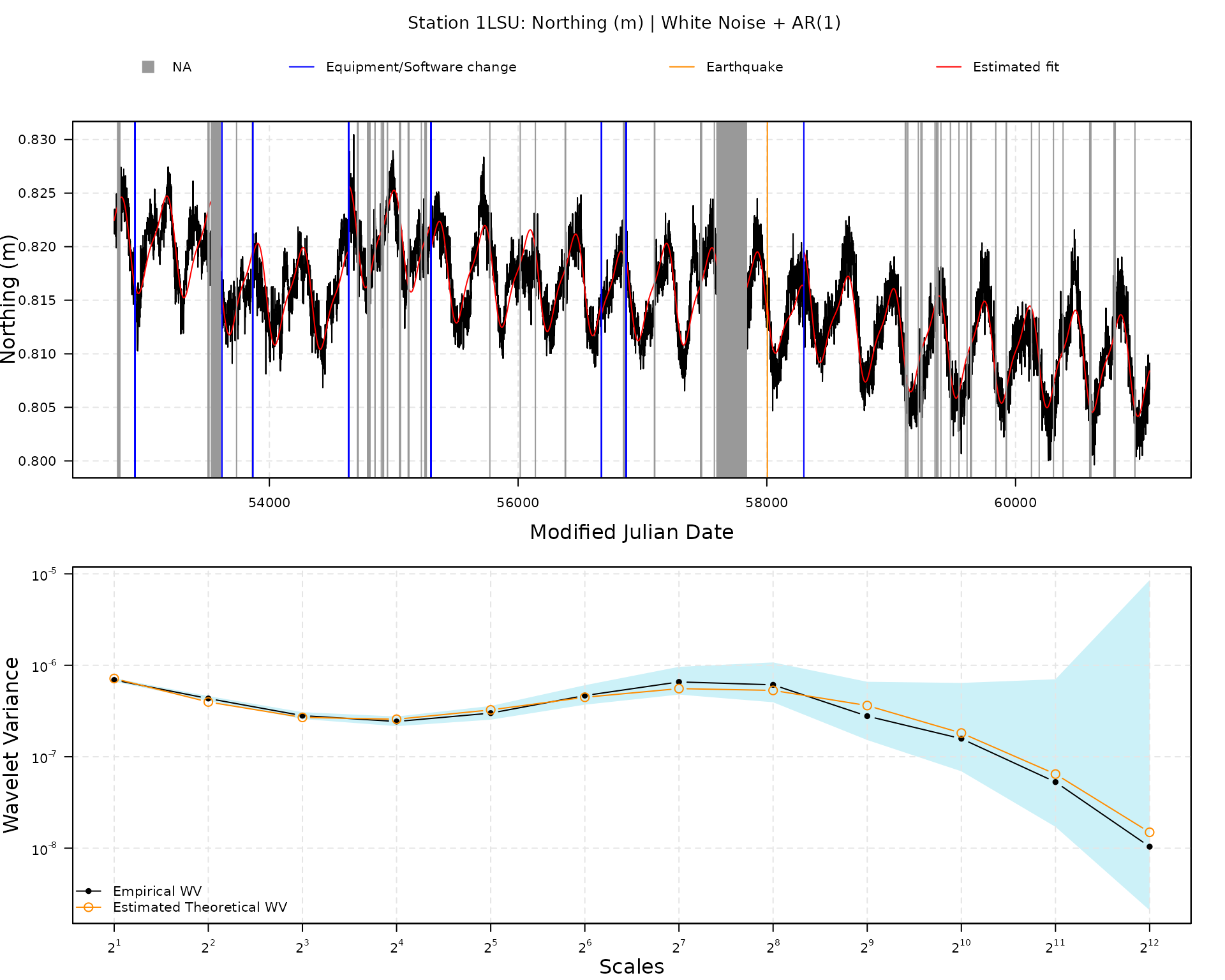
## GMWMX fit GNSS Times Series (Nevada Geodetic Laboratory)
## Estimate Std.Error CI.Lower CI.Upper
## Intercept 8.156e-01 2.265e-03 8.112e-01 8.200e-01
## Trend -1.090e-06 4.736e-07 -2.018e-06 -1.613e-07
## Sin (Annual) -5.216e-04 2.248e-04 -9.623e-04 -8.096e-05
## Cos (Annual) -4.129e-03 2.264e-04 -4.573e-03 -3.685e-03
## Sin (Semi-Annual) 1.089e-03 1.493e-04 7.964e-04 1.382e-03
## Cos (Semi-Annual) -4.455e-04 1.494e-04 -7.384e-04 -1.526e-04
## Jump: MJD 52920 4.958e-04 1.369e-03 -2.187e-03 3.179e-03
## Jump: MJD 53619 -3.057e-03 1.254e-03 -5.514e-03 -5.996e-04
## Jump: MJD 53866 -5.586e-04 1.247e-03 -3.003e-03 1.886e-03
## Jump: MJD 54637 -2.499e-04 2.009e-03 -4.187e-03 3.687e-03
## Jump: MJD 54640 6.393e-03 2.010e-03 2.453e-03 1.033e-02
## Jump: MJD 55300 -2.496e-03 9.734e-04 -4.404e-03 -5.887e-04
## Jump: MJD 56671 -1.193e-03 1.302e-03 -3.745e-03 1.359e-03
## Jump: MJD 56868 1.120e-03 1.297e-03 -1.421e-03 3.661e-03
## Jump: MJD 58298 3.321e-03 1.969e-03 -5.392e-04 7.181e-03
## Jump: MJD 58004 1.137e-03 1.484e-03 -1.771e-03 4.045e-03
## Earthquake: MJD 58004 -7.135e-03 3.385e-03 -1.377e-02 -5.004e-04
##
## Missingness model
## Proportion missing : 0.0584
## p1 : 0.0073
## p2 : 0.1173
## p* : 0.9416
##
## Stochastic model
## Sum of 2 processes
## [1] White Noise
## Estimated parameters : sigma2 = 1.434e-06
## [2] AR(1)
## Estimated parameters : phi = 0.9803, sigma2 = 1.35e-07
##
## Runtime (seconds)
## Total : 2.3920
plot(fit4)