This vignette shows how to build stochastic models, combine them with
+, generate data, and plot the results.
Available models
You can build a single stochastic process with any of the following model constructors:
-
wn()(white noise) -
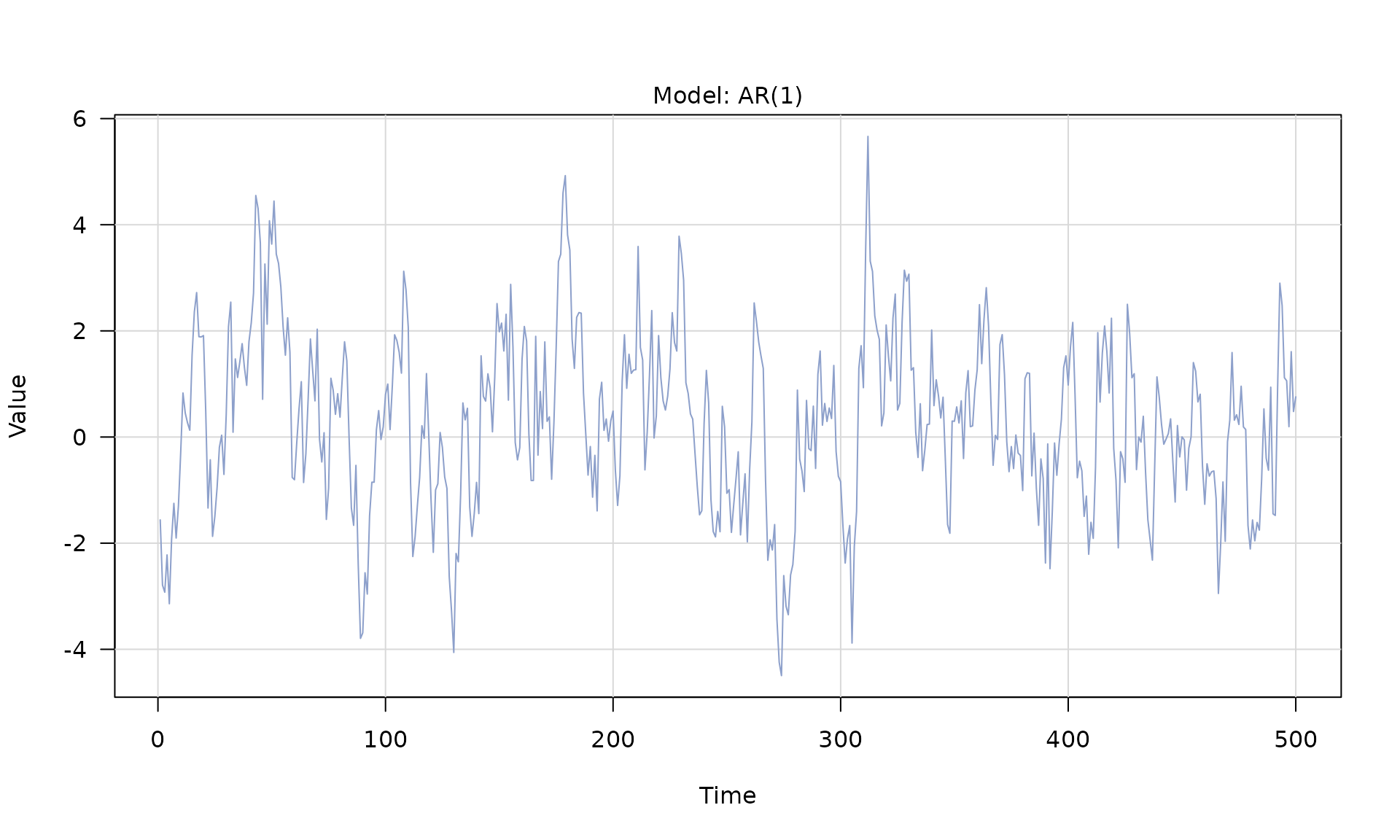
ar1()(AR(1)) -
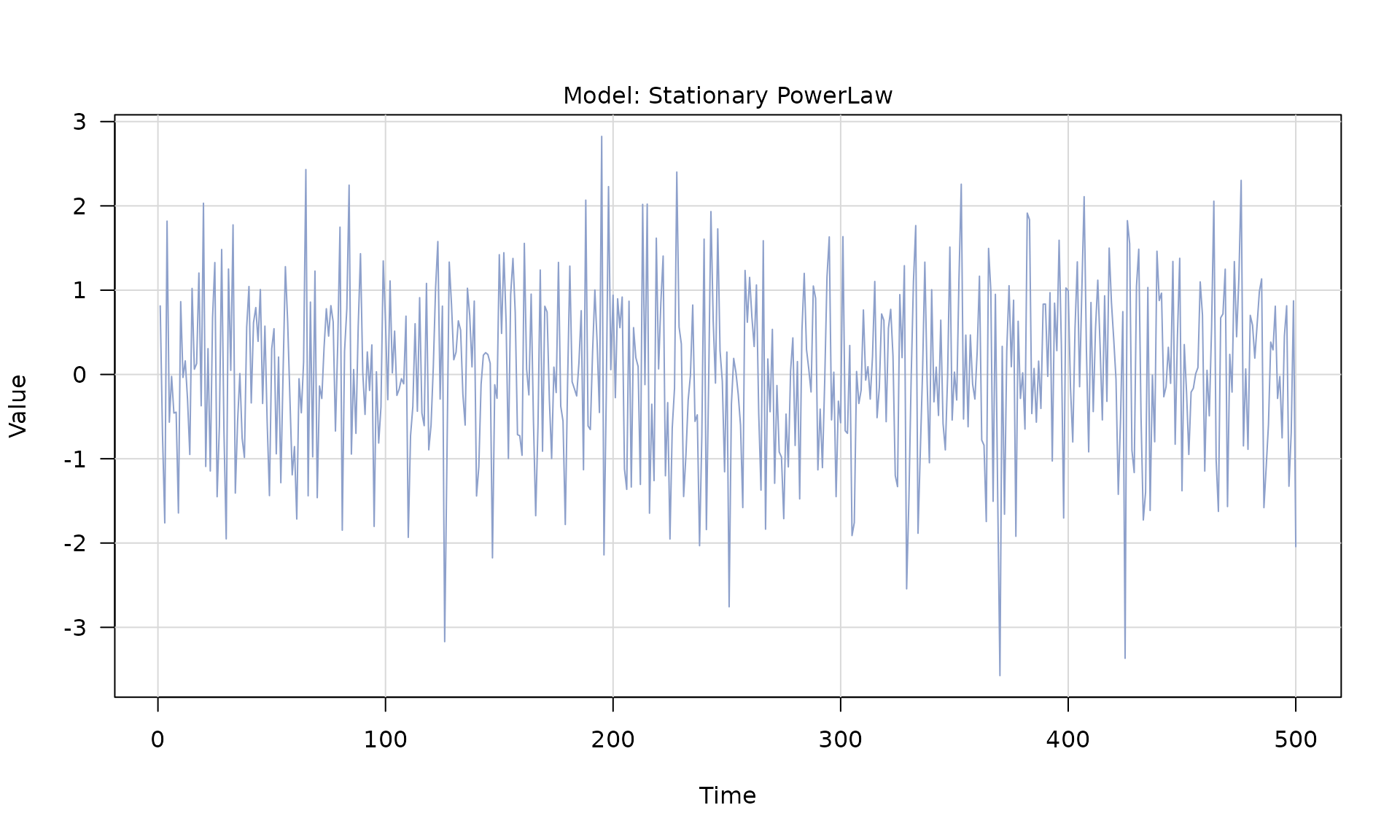
pl()(power-law) -
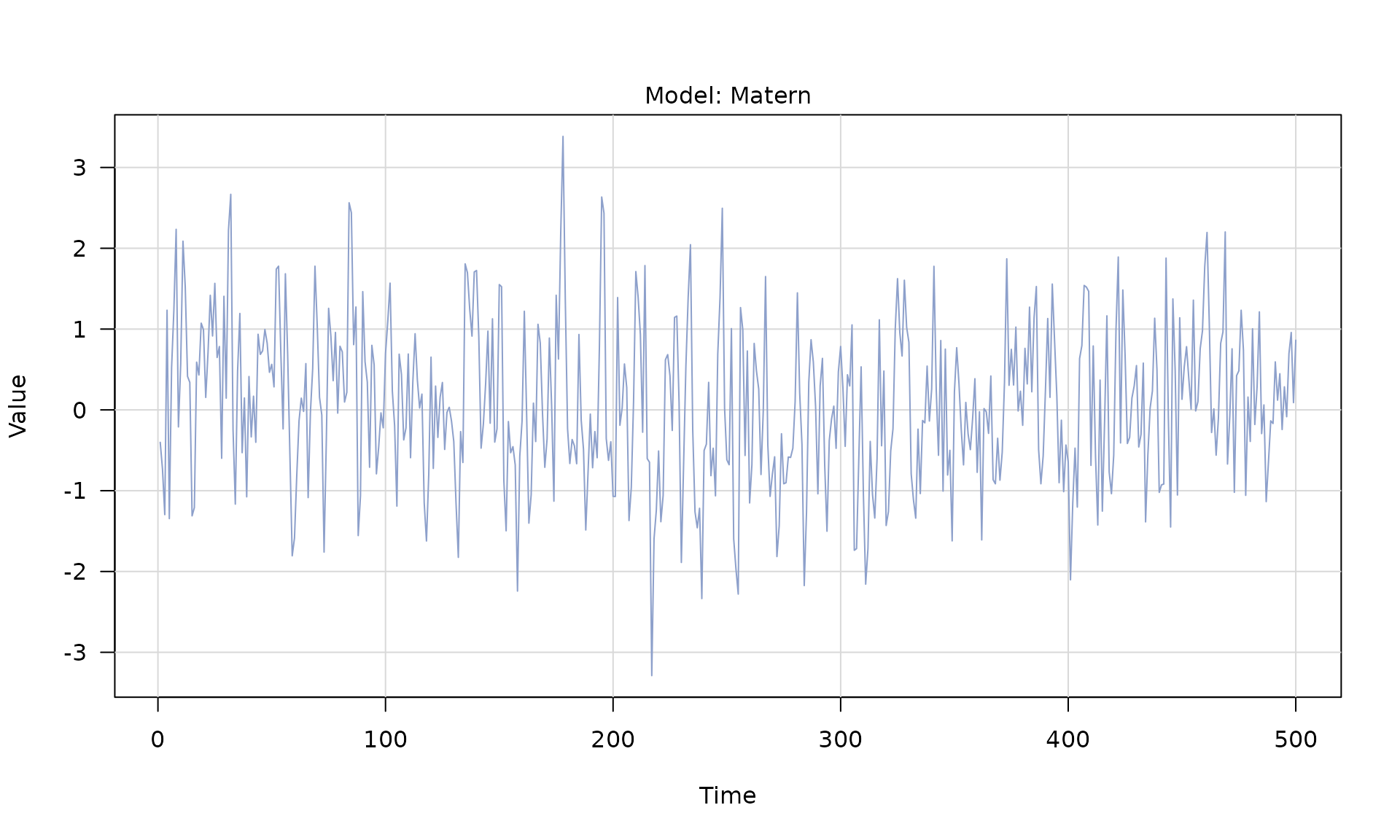
matern()(Matérn) -
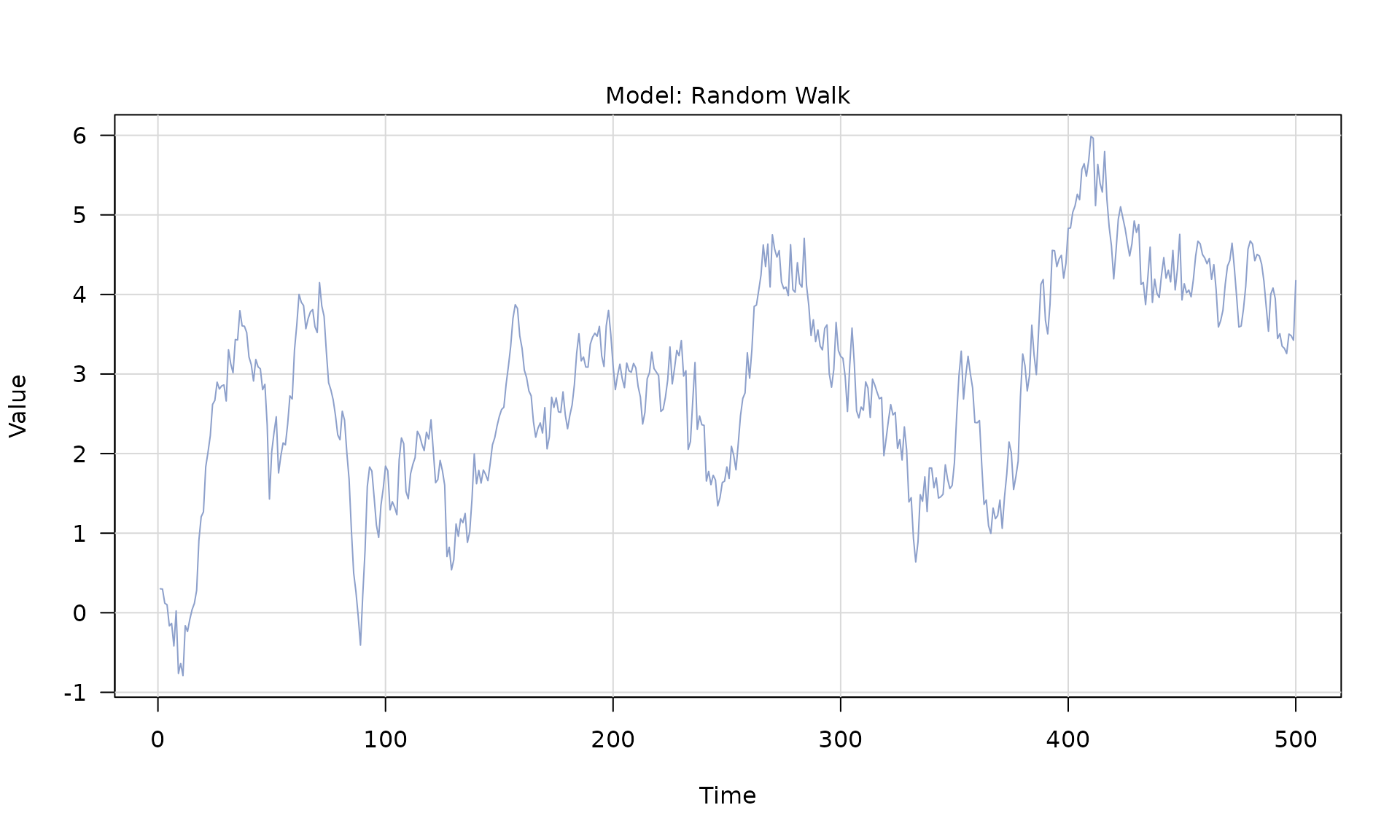
rw()(random walk) -
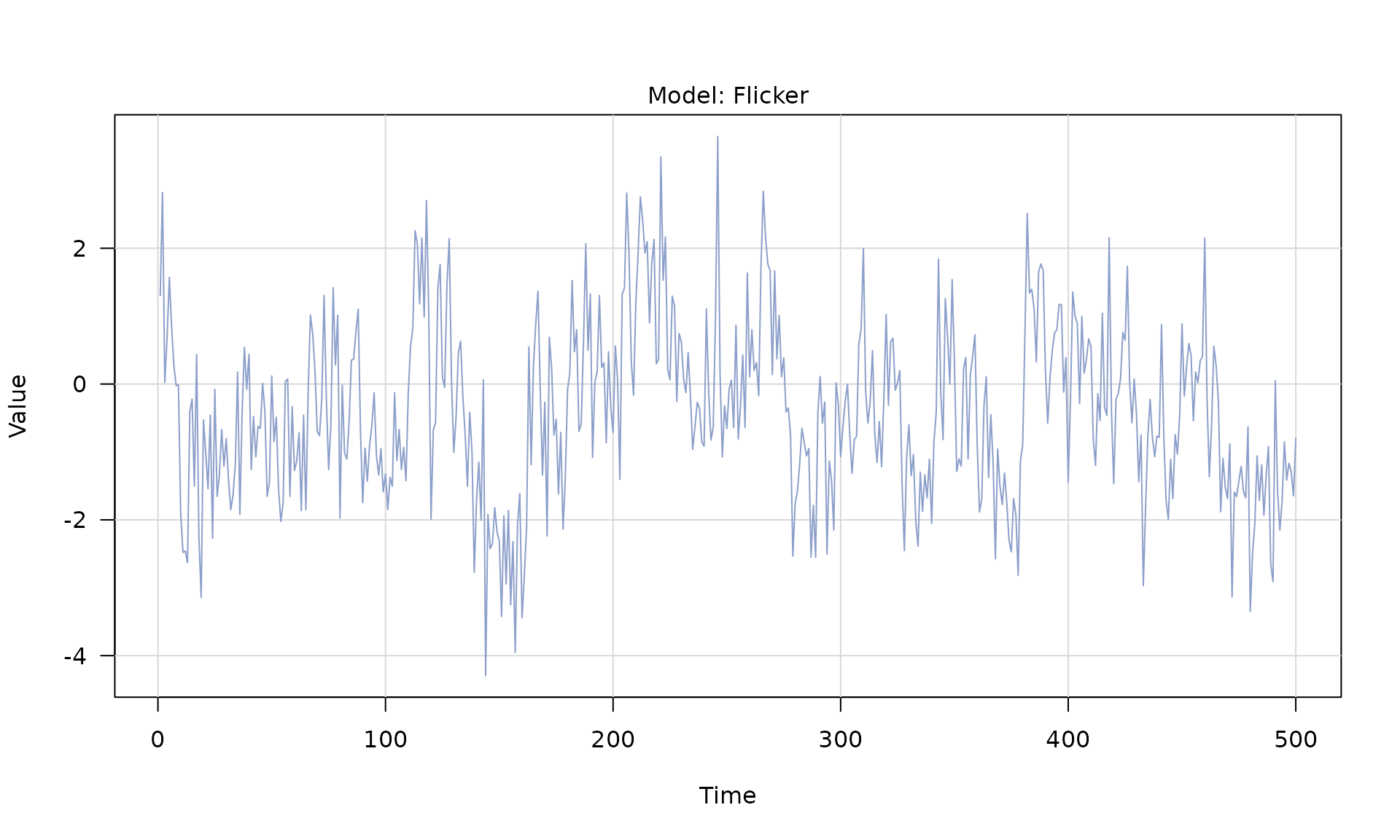
flicker()(flicker)
Each constructor returns a time_series_model object that
can be plotted or combined with others using +.
Stochastic models
White noise
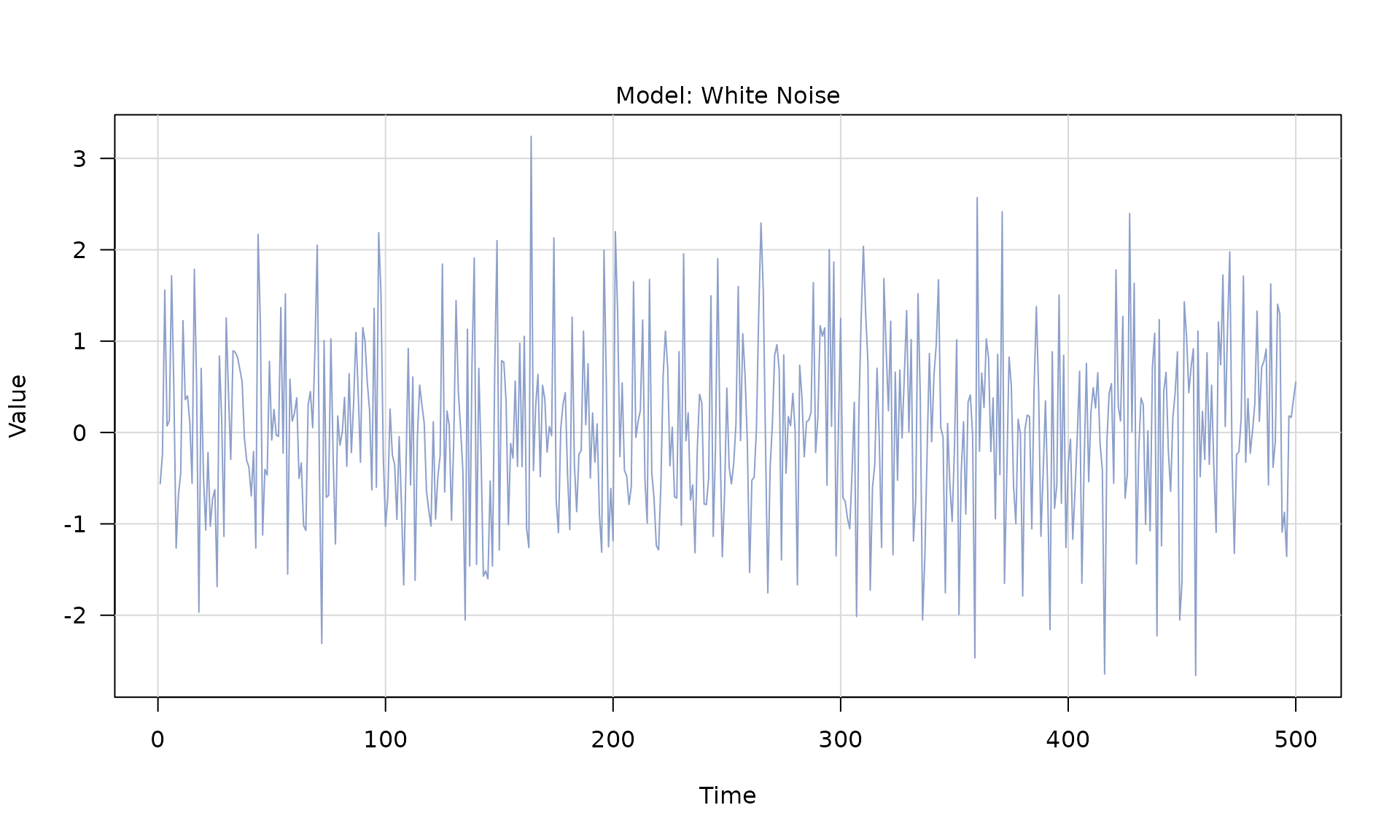 The generated object is a
The generated object is a generated_time_series with a
numeric series in $series:
head(series_wn$series)## [1] -0.56047565 -0.23017749 1.55870831 0.07050839 0.12928774 1.71506499Reproducible generation
You can set a random seed before calling generate(), or
pass a seed directly to generate(), to make the output
deterministic. Using the same seed and model parameters produces the
exact same time series.
model_wn <- wn(sigma2 = 1)
set.seed(1234)
series_a <- generate(model_wn, n = 100)
series_b <- generate(model_wn, n = 100, seed = 1234)
series_c <- generate(model_wn, n = 100, seed = 4321)
all.equal(series_a$series, series_b$series)## [1] TRUE
all.equal(series_a$series, series_c$series)## [1] "Mean relative difference: 1.310458"Composite models (sum of processes)
Use + to build a composite model from multiple
stochastic processes. The result is a sum_model that can be
passed to generate().
## [1] "sum_model"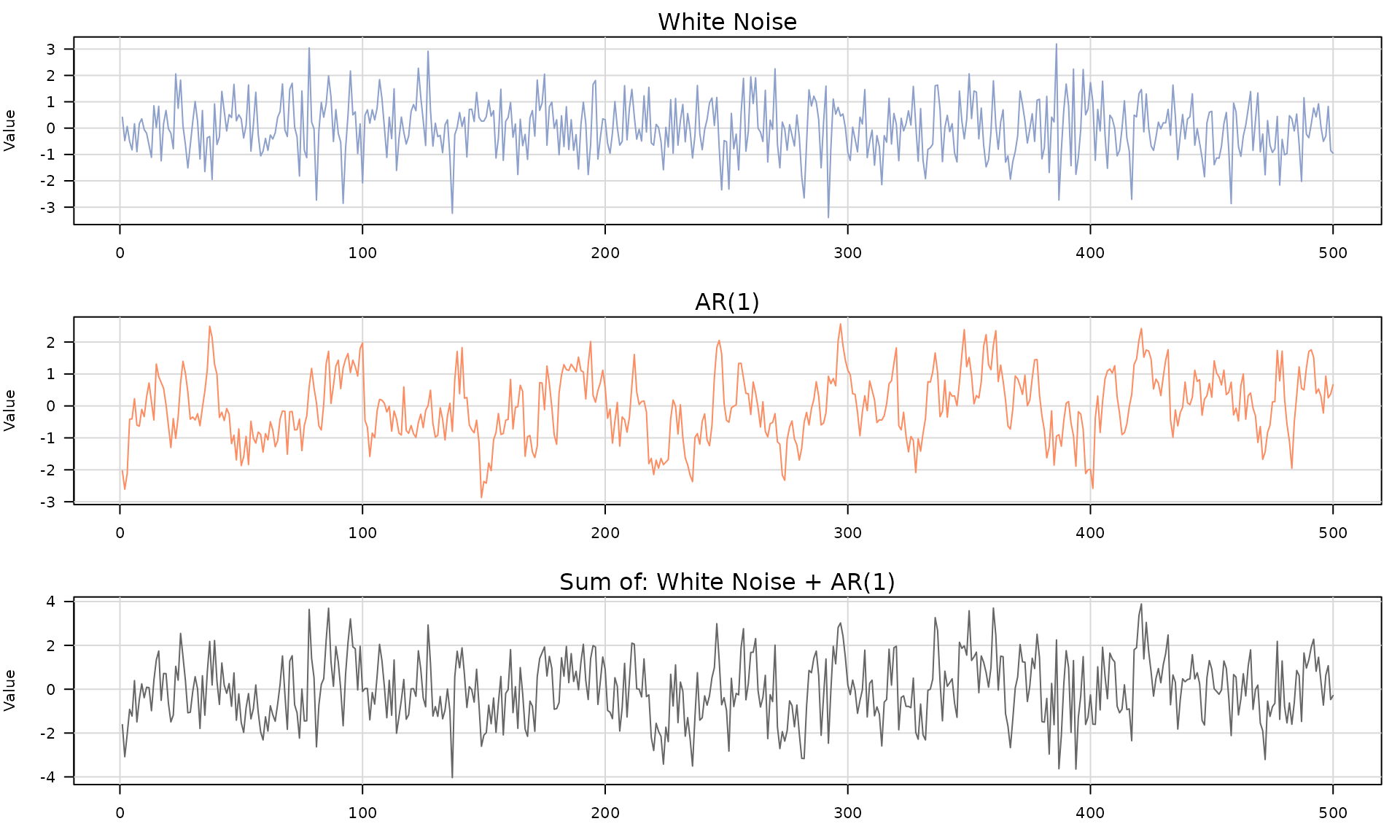
The composite output is a
generated_composite_model_time_series with:
-
series(the total sum) -
components(a list of each component series) -
n(length of the series) -
model(names of each component) -
parameters(parameters of each component)
names(series_wn_ar1)## [1] "series" "components" "n" "model" "parameters"